Incomplete Dominance and Codominance
In genetics, not ALL traits are purely dominant and recessive. Some traits show incomplete dominance or codominance. We will investigate both types.
Incomplete Dominance
If Mendel were given a female black mouse and a male white mouse, and asked what their offspring would look like, he would have predicted that a certain percentage be white and a certain percentage be black, but he would have never predicted a GRAY mouse! For Mendel, the phenotype of the offspring resembled the phenotype of at least one of the parents. Mendel was unaware of the phenomenon of INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE.
With incomplete dominance, a cross between organisms with two different phenotypes produces offspring with a third phenotype that is a blending of the parental traits.
Think of incomplete dominance like mixing paint. If you mixed red and white paint, what color would you get?
Red doesn’t totally block (dominate) the white, instead there is incomplete dominance and we end up with something in-between.
Setting up a Punnett square to solve for incomplete dominance:
-Both letters are capital (equally dominant)
-TWO different letters are used to distinguish each trait.
 |
![]()
1. A cross between a purple babble bird and a white babble bird produces offspring that are lavendar. The color of the babble bird is determined by just 2 alleles.
a) What are the genotypes of the parent babble birds in the original cross?
Purple babble bird=
White babble bird=
b) What is/are the genotype(s) of the lavender offspring?
c) What would be the phenotypic ratios of the offspring produced by 2 lavender babble birds?
2. The color of fruit for the Deidre Flower is determined by 2 alleles When two plants with are crossed the following phenotypic ratios are present in the offspring:
25% red flowers, 50% orange flowers, and 25% yellow flowers
What are the phenotypes and genotypes of the parent Deidre flowers that produced the offspring above?
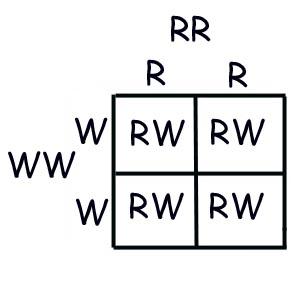
Co-Dominance
The prefix “co” means “together”. Cooperate- work together. Coexist- exist together, etc.
In codominance, the “Recessive” and “Dominant” traits appear together in the phenotype of hybrid organisms. A cross between organisms with two different phenotypes produces offspring with a third phenotype in which both of the parental traits appear together. Neither trait is lost!
If you were to cross a red and white flower, what do you think the offspring would look like?): ______________________________
When setting up a Punnett square to solve for codominance, the same rules we used to solve for incomplete dominance apply.
 |
-Two different letters, one for each trait.
-Both letters should be capitalized.

1. Some cows can have red fur, white fur, or a mixture of both red and white hairs (called roan). Predict the phenotypic ratios of offspring when a homozygous white cow is crossed with a roan bull.
2. A cross between a black cat and a tan cat produces a tabby pattern (black and tan fur together).
- What pattern of inheritance does this illustrate?
- What percent of kittens would have tan fur if a tabby cat is crossed with a black cat?